
5 Steps to Quality Oversight of Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)

Summary
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly using contract manufacturing organizations (CMO) to reduce overheads and overall costs, and speed up the drug development timelines. While outsourcing provides several advantages, it also presents many challenges.- Author Company: ComplianceOnline
- Author Name: Ashutos Swain
- Author Email: referral@complianceonline.com
- Author Website: https://www.complianceonline.com/resources/quality-oversight-of-pharmaceutical-contract-manufacturing-organizations.html?channel=pharmiweb
1. The challenges
Organizations that outsource do not have direct control over the CMO operations. Most of the CMOs deal with multiple clients and their manufacturing, laboratory, & quality systems are designed to allow them maximum flexibility. Additionally, there are different compliance/GMP philosophies. Companies that use CMOs are ultimately responsible for the product quality, safety, efficacy, and cGMP compliance. When issues at the CMOs are identified during audits, the organization that uses the CMOs receive warning letters and not the CMOs.
2. Overcoming the challenges with proper oversight and controls
If your organization is using CMOs, you can overcome the challenges by ensuring that all personnel responsible for CMO oversight learn and apply the full circle of CMO management.
The steps to exercising proper oversight and controls are given below:

Proper qualification and auditing
"ICH guidance for industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System states that, as part of a pharmaceutical quality system, the owner is ultimately responsible for ensuring that "processes are in place to assure the control of outsourced activities and quality of purchased materials." It indicates that these processes should incorporate quality risk management and include the following critical activities:
- Assessing the suitability and competence of potential contractors before outsourcing operations or selecting material suppliers. This could be accomplished through audits, material evaluations, or other qualification criteria."
- Structure your organization
As already discussed, the sponsor organization has the ultimate responsibility for product compliance, product, quality, safety, and efficacy. This responsibility calls for structuring your organization to exercise proper oversight over manufacturing, quality control labs, quality assurance, regulatory affairs, and project management.
- Ensure that the personnel in your organization who are involved in the key areas have relevant knowledge and experience including technical expertise and authoring capabilities
- Define key oversight roles and include specific sponsor-CMO responsibilities in the quality agreement.
- Document appropriate oversight details' have standard SOPs
- General Prerequisites' CMO evaluation Questions
- What is the experience and regulatory history of the CMO?
- What is the level of adherence to GMPs and SOPs
- What is the quality of content in the required CMO documents?
- What is the level of hand-holding required?
- What is the depth and breadth of the CMOs practical experience?
- Is CMO available to formulate and fill when needed?
- Is there sufficient staffing to allow for late-stage changes in your production plan?
- Is the CMO management team experienced and competent?
- What are the CMOs best practices?
- Does the CMO fit into your budget?
- Is their culture aligned with yours?
- Do they allow on-site audits?
- Are there barriers to communications such as language and time zone differences?
- Does the CMO have a system in place to avoid the use of client names/initials, locks information in a secure area and send the client separate passwords for electronic access to documents, under a separate cover?
- Prerequisites to consider in key areas
Manufacturing
- What is the CMO's expertise in manufacturing type/equipment?
- Can the CMO author transfer documents/batch records?
- Can the CMO effectively correct manufacturing Issues?
Quality control labs
- What is the CMO's expertise in Analytical Methodology / Equipment?
- Does the CMO have the ability to Author Analytical Methods / Validation Protocols?
- Does the CMO have proper processes to address laboratory issues?
- Does the quality department appear actively involved or is there a rigid system in place that may not accommodate the product's specific needs?
Quality assurance
- What are the CMO's competencies with respect to quality assurance?
- Can the CMO author deviations/CAPAs, OOS, change controls?
- Does the CMO have proper processes to address quality issues?
Regulatory affairs
- Does the CMO have an understanding of the regulatory environment in which a product will be evaluated?
- Does the CMO have specific capabilities, experience and production environment to meet the product's specific requirements?
- Has the CMO been audited by several companies and regulatory agencies?
Regulatory affairs
- Does the CMO have an understanding of the regulatory environment in which a product will be evaluated?
- Does the CMO have specific capabilities, experience and production environment to meet the product's specific requirements?
- Has the CMO been audited by several companies and regulatory agencies?
Project management
- Does the CMO understand all sponsor requirements?
- Is the CMO capable of maintaining and adhering to project plans?
- Does the CMO have a strong sense of partnership and a high level of commitment in partnering with you?
- Is there a clear process to keep the lines of communication open?
The next critical activity stated in the ICH guidance for industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System includes
- "Defining the manufacturing responsibilities and communication processes for quality related activities of the involved parties. For outsourced activities, these should be in a written agreement."
The key elements of a quality management agreement include
- "Purpose/Scope - to cover the nature of the contract manufacturing services to be provided
- Definitions - to ensure that the owner and contract facility agree on precise meaning of terms in the quality agreement
- Resolution of disagreements - to explain how the parties will resolve disagreements about product quality issues or other problems
- Manufacturing activities - to document quality unit and other activities associated with manufacturing processes as well as control of changes to manufacturing processes
- Life cycle of, and revisions to, the quality agreement
The most critical pieces are quality and change control include:
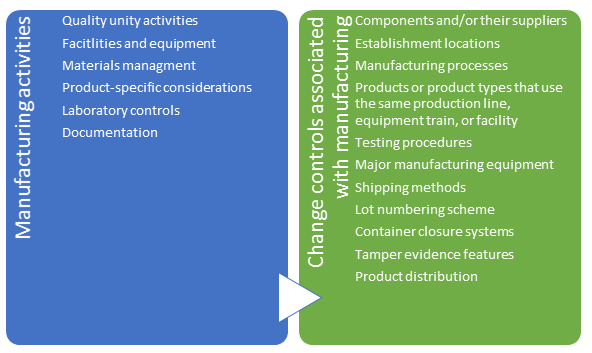
Employ personnel with deep technical and authoring capabilities in the following key areas including
- Manufacturing
- Chemistry / QC Laboratory
- Quality Assurance
- Regulatory Affairs
- Project Management
Proactive reviews and approvals of documents provided by CMOs
The next critical activity stated in the ICH guidance for industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System includes
- "Monitoring and reviewing the performance of the contract facility and identifying and implementing any needed improvements."
Proactive reviews are critical to the success of CMO management.
- "Either an owner or a contract facility may initiate changes to processes, equipment, test methods, specifications, and other contractual requirements. How all changes are managed should be outlined in the agreement, including allocation of responsibilities for conducting validation activities as needed before implementing changes."
- "The owner and contract facility should carefully consider and agree on the types of changes to report to each other and to FDA and the need for approval from each party's quality unit and FDA, as applicable."
Sponsor final reviews of APIs and drug products
The next critical activity that is stated in the ICH guidance for industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System includes
- "Monitoring incoming ingredients and materials to ensure they are from approved sources using the agreed-upon supply chain."
Regulatory References
Contract Manufacturing Arrangements for Drugs: Quality Agreements Guidance for Industry
- "Owners are responsible for approving or rejecting drugs manufactured by the contract facility, including for final release. In all cases, the owner must not introduce or deliver into interstate commerce, or cause to be introduced or delivered into interstate commerce, any drugs that are adulterated or misbranded."
Exercise controls
- For both owners and contract facilities that conduct manufacturing operations, CGMP "includes the implementation of oversight and controls over the manufacture of drugs to ensure quality, including managing the risk of and establishing the safety of raw materials, materials used in the manufacturing of drugs, and finished drug products."
Use a comprehensive quality systems model
- "Owners can use a comprehensive quality systems model to help ensure compliance with CGMP.Quality agreements should clearly describe the materials or services to be provided, quality specifications, and communication mechanisms between the owner and contract facility."
ICH guidance for industry
- Evaluate contract facilities to ensure that contractor sites comply with CGMP for specific operations
- Have approved written agreements with contractors that define the manufacturing responsibilities in detail, including the quality measures, of each party.
- The written agreements should also define considerations for subcontracting; describe how changes to processes, equipment, methods, and specifications will be managed; and permit the owner to audit its contractor's facilities for compliance with CGMP.
FDA Safety & Innovation Act (FDASIA- 2012):
- "FDASIA includes a set of provisions, contained in Title VII of the statute, which give FDA new authorities to address the challenges posed by an increasingly global drug supply chain."
Eudralex, Vol. 4, Ch.7- Outsourced Activities
- "The pharmaceutical quality system of the Contract Giver should include the control and review of any outsourced activities. The Contract Giver is ultimately responsible to ensure processes are in place to assure the control of outsourced activities."
Eudralex, Vol. 4, Ch. 5- Production
- "The holder of the manufacturing authorisation shall verify such compliance either by himself or through an entity acting on his behalf under a contract."
Attend the seminar 'Effective Quality Oversight of Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)' to understand how to manage CMOs - from start to finish. The seminar will shed in-depth light on Selection and Qualification, Quality Agreements, Understanding of CMO Operations, and Review of Key CMO Records. This practical how-to course, is designed to provide participants with skills they can immediately apply to CMO oversight within their own organizations.
The speaker Andrew Campbell has 25 years of pharmaceutical quality assurance and quality systems experience in both industry and consulting roles. Mr. Campbell has worked in clinical supply and commercial manufacturing environments, and has experience with integrated manufacturing and contract manufacturing business models. He has extensive expertise in the areas of deviation - CAPA, change control, GMP auditing, GMP training, and regulatory inspection preparation and management.
