
Respiratory System Primary Cells

Summary
Human pulmonary cells, a mainstay of many medical research labs, have acquired new relevance in the era of COVID-19. As the SARS-CoV-2 virus causes serious complications most commonly in the lungs, human primary pulmonary cells have become increasingly important in the study of this coronavirus strain.- Author Company: AcceGen
- Author Name: AcceGen R&D Team
- Author Email: marketing@accegen.com
- Author Telephone: +18626862696
- Author Website: https://www.accegen.com
The human respiratory system is composed of a network of tissues and organs that enable the body to absorb oxygen from the air as well as expel carbon dioxide and other waste gasses. These functions are supported by a variety of cells that aid in promoting epithelial homeostasis, preventing alveolar collapse, facilitating the exchange of gasses between the blood and the tissues, and ensuring that the lungs adjust properly to low atmospheric pressure.
Primary cells taken directly from the respiratory tissue of a human subject can simulate in vivo conditions with a very high degree of accuracy and, for that reason, have granted researchers a number of insights into various lung diseases and related medical disorders.
Types of Respiratory System Cells
The cells of the respiratory system can be grouped into three distinct categories. These are:
●
Nasal cells – These can be found in the mucosal epithelium of the nasal cavity.
●
Bronchial/Tracheal cells – Taken from the linings of the trachea (the “windpipe,” connected to the larynx) and the bronchi (branched airways connected to the trachea), which all work together to convey air from the atmosphere into the lungs.
●
Pulmonary cells – Cells from human lung tissue can be divided into four subtypes:
○
Epithelial cells– Regulate immune response, clear away particulate matter, and provide barrier protection.
○
Endothelial cells– Manage vascular homeostasis.
○
Smooth muscle cells– Maintain healthy bronchial tone.
○
Fibroblasts– Promote recovery from injury and inflammation.
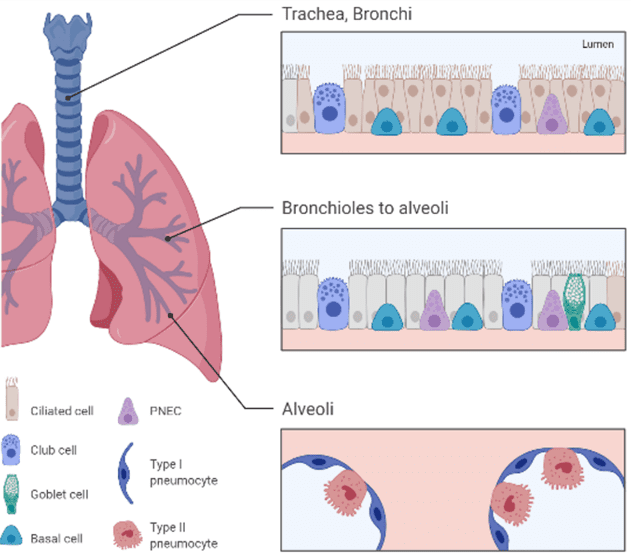 Figure1. Respiratory System Cell Types
Figure1. Respiratory System Cell Types
Uses of Respiratory System Cells
Primary cells from the respiratory system are useful in many research laboratory applications. Bronchial/tracheal cells continue to yield valuable discoveries relating to the causes and progression of respiratory disorders such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Human nasal epithelial cells (HNEpC), which are sensitive to environmental pollutants, are commonly utilized to study the characteristics of viral infections.
Human pulmonary cells, a mainstay of many medical research labs, have acquired new relevance in the era of COVID-19. As the SARS-CoV-2 virus causes serious complications most commonly in the lungs, human primary pulmonary cells have become increasingly important in the study of this coronavirus strain.
AcceGen offers 41 different types of human respiratory system primary cells that are well suited for research use. Available primary cells include Human Nasal Epithelial Cells (HNEpC), Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (HBEpC), and Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells (PAEpiC2). For more information, visit us online at https://www.accegen.com.
About AcceGen
Since 2016, the leading biotech company AcceGen has distributed custom genomic research solutions to researchers and laboratories across a wide variety of industries, such as the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and specialty ingredients sectors. AcceGen is based out of Fairfield, New Jersey.
META: AcceGen, a New Jersey-based biotech company, explains how its various respiratory system primary cells are useful in many medical research applications.
